Flat Cables vs. Round Cables in Photovoltaic Systems: Which One to Choose?
- Share
- Issue Time
- Feb 14,2025
Summary
In this article, we'll compare flat cables and round cables, examining their key differences, benefits, and drawbacks, and help you decide which one is best for your specific photovoltaic projects.
Flat & Round PV Wire
When designing and installing photovoltaic (PV) systems, one of the most critical decisions involves choosing the right cables. The performance, durability, and efficiency of your installation depend heavily on the cables that connect the various components of the system. Two of the most common cable types in PV installations are flat cables and round cables. Both have their advantages and are suited to different scenarios.
In this article, we'll compare flat cables and round cables, examining their key differences, benefits, and drawbacks, and help you decide which one is best for your specific photovoltaic projects.
What Are Flat Cables?

Flat cables are electrical cables designed with conductors arranged in a flat, parallel configuration, typically encased in a thin, flexible insulating material. These cables are often used in applications where space is limited or when high-density wiring is required.
Key Features of Flat Cables:
Space-Efficient Design: The flat shape allows cables to sit flush against surfaces, making them ideal for installations in tight spaces, such as between solar panels or along flat roofs.
Flexible and Easy to Install: Their design makes flat cables more pliable, which is helpful in installations where the cable needs to bend and navigate through small spaces.
Suitable for Controlled Environments: Flat cables are best used indoors or in locations where the weather or environmental conditions aren’t extreme, as they aren’t as durable as round cables in harsh conditions.
What Are Round Cables?
Round cables, in contrast, consist of one or more conductors twisted together and encased in a rounded, flexible jacket. These cables are often used in PV systems where flexibility, durability, and long-distance transmission are essential.
Key Features of Round Cables:
High Durability: Round cables are generally more durable and resistant to damage from environmental factors such as UV rays, moisture, and extreme temperatures. They are designed to withstand harsh conditions, making them ideal for outdoor and large-scale PV installations.
Flexible Over Long Distances: Due to their twisted construction, round cables offer superior flexibility, which makes them easier to route over longer distances compared to flat cables.
Heavy-Duty Insulation: Round cables are typically coated with a thicker, more robust insulating layer to provide added protection against physical damage and environmental stress.
Round Solar Cable Conductor: The individual conductors in round cables are typically twisted or bundled, which increases the strength and flexibility of the cable.
Better for Heavy Loads: Round cables are often designed to carry higher electrical loads, making them ideal for high-capacity systems such as utility-scale solar power plants.
Key Differences Between Flat and Round Cables in PV Systems
When comparing flat solar cables and round solar cables, it's essential to understand how each type performs in various aspects, from flexibility and durability to cost-effectiveness.
Physical Structure and Flexibility
Flat Cables: The flat construction makes these cables ideal for installations in narrow spaces, such as in solar panel wiring, where multiple cables need to be organized tightly. However, this design also limits their flexibility over long distances.
Round Cables: The round shape allows for greater flexibility over longer distances, which is why round cables are often used in large-scale installations where cables need to stretch across wide areas, such as from the array to the inverter or junction boxes.

Durability and Resistance
Flat Cables: These cables are not as durable when exposed to the elements. They are more prone to wear and tear under UV radiation and extreme weather conditions. As a result, flat cables are better suited for indoor or controlled-environment applications.
Space Efficiency
Flat Cables: One of the biggest advantages of flat solar cables is their ability to save space. The flat configuration allows for tight, organized installations where space is limited. This feature is particularly useful for residential rooftops or in situations where minimizing the cable footprint is a priority.
Round Cables: Round cables take up more space compared to flat cables and are more challenging to manage in confined areas. However, they are easier to route in open areas where space is less of a concern.
Cost Considerations
Flat Cables: Due to their simpler design and lighter weight, flat cables tend to be more cost-effective, making them an attractive option for smaller-scale PV projects with lower power requirements.
Round Cables: Round cables tend to be more expensive, largely due to their higher durability and construction for outdoor use. However, the additional cost is often justified for large-scale PV installations or systems located in harsh environments where durability is paramount.
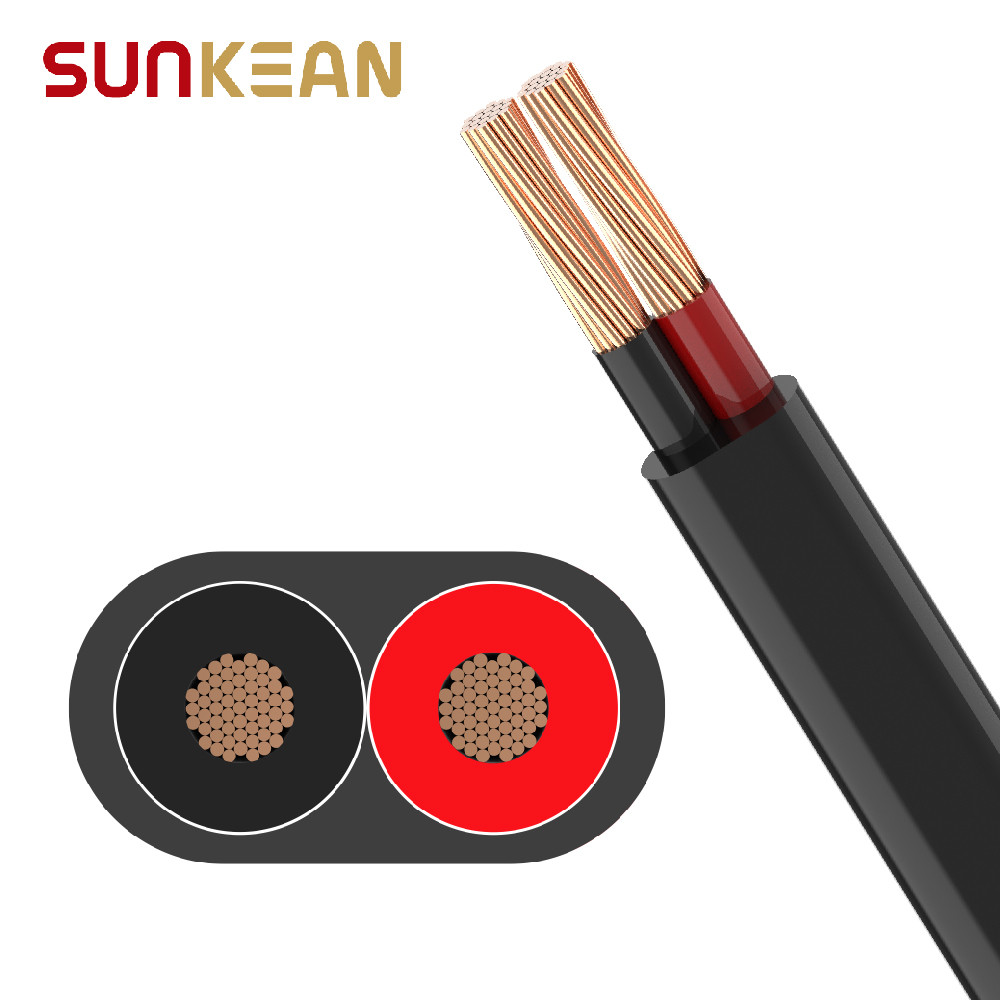
Conductor: 14AWG~10AWG
Insulation Color: Optional color
Jacket Color: Black
Conductor: 14AWG~10AWG
Insulation Color: Optional color
Jacket Color: Black
This cable can be used for photovoltaic inverter AC branch lines.
This cable can be used for photovoltaic inverter AC branch lines.
When to Use Flat Cables vs. Round Cables in PV Projects?
Choosing the right cable type for your PV installation depends on several factors, including the scale of the project, environmental conditions, and space requirements.
Use Flat Cables When:
Space is Limited: If you're working in tight spaces or need to bundle multiple cables together in a confined area, flat cables are a great option. They are easier to manage and organize in small spaces, such as on rooftops or between solar panels.
Indoor or Controlled Environments: Flat cables are more suited for indoor applications or areas where environmental factors like UV exposure or extreme temperatures are not a concern.
Cost is a Concern: For smaller projects or where budget constraints are an issue, flat solar cables are a more cost-effective solution.
Use Round Cables When:
Durability is Key: Round solar cables excel in harsh outdoor environments where exposure to the elements, including UV rays, moisture, and extreme temperatures, is a concern. These cables are often used in commercial and industrial-scale PV systems where long-term performance is crucial.
Long-Distance Runs Are Needed: If your PV installation requires cables to span large distances—such as between the solar array and the inverter or the inverter and the utility grid—round cables offer the flexibility needed to navigate these distances with ease.
Heavy Power Loads: For large, high-capacity PV systems, round cables are better suited to handle higher electrical loads, making them ideal for large-scale commercial and utility-scale projects.
Pros and Cons of Flat vs. Round Cables in PV Applications

Flat Cables
Pros:
Space-efficient for compact installations
Easier to manage in tight spaces
Lightweight and flexible for quick installations
Cost-effective, making them ideal for smaller projects
Cons:
Less durable in harsh environmental conditions
Limited flexibility over long distances
Not suitable for heavy-duty applications
Round Cables
Pros:
Superior durability for outdoor and high-demand environments
Flexible over long distances, making them ideal for large-scale installations
Strong resistance to UV radiation, moisture, and extreme temperatures
Capable of carrying higher electrical loads
Cons:
Bulky and harder to install in confined spaces
More expensive than flat cables
Heavier, requiring more labor to manage and install

